Producing hydrogen from water: new technology, record production
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
A team led by Kyriakos Stylianou from Oregon State University has developed a material capable of efficiently transforming sunlight and water into hydrogen. This hydrogen can be used in cars and in the production of many products.
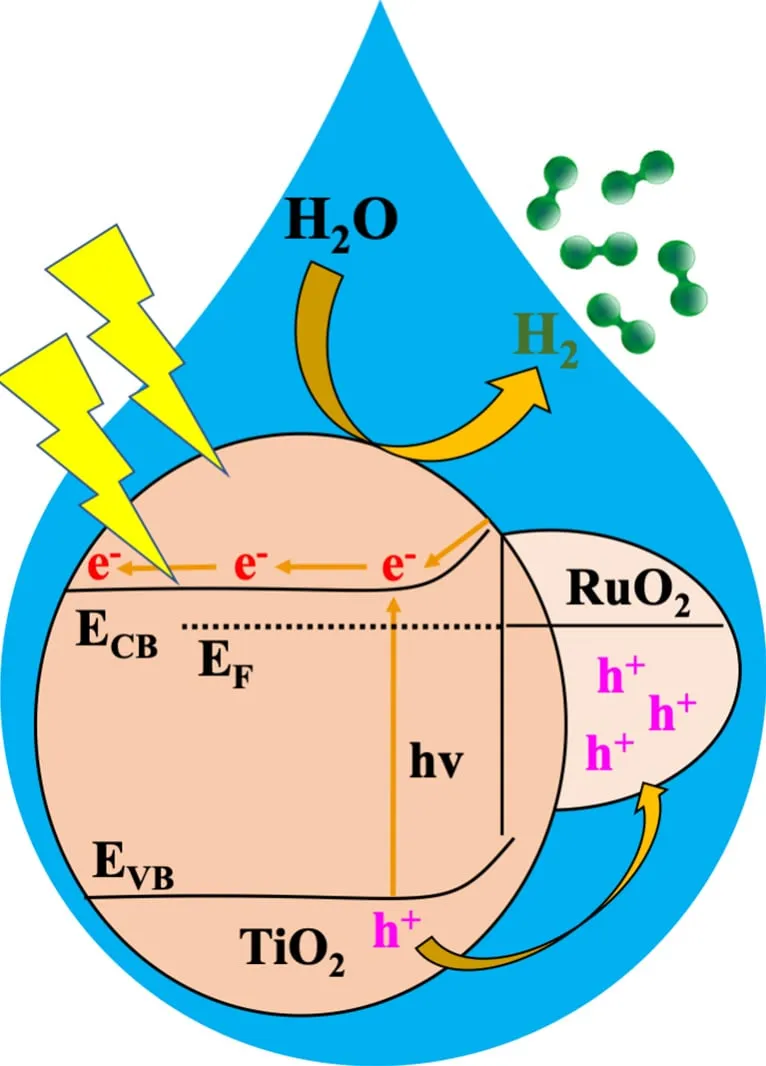
Water splitting by photocatalysis.
Credit: Kyriakos Stylianou
Stylianou and his team worked on materials called Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOF). These materials are composed of metals and organic molecules, forming structures with tiny pores and tunable properties.
The researchers used an MOF to create a catalyst that, when exposed to sunlight, quickly and efficiently splits water into hydrogen. This catalyst, called RTTA, is comprised of two materials: ruthenium oxide and titanium oxide, doped with sulfur and nitrogen.
Among the various materials tested, RTTA-1 showed the best results, producing hydrogen very quickly and with great efficiency. In one hour, one gram of RTTA-1 produced more than 10,700 micromoles of hydrogen, effectively using 10% of the received light.
This performance is due to the synergistic properties of the metal oxides and the surface properties of the parent MOF. This discovery highlights the potential of metal oxide heterojunctions derived from MOFs for practical hydrogen production.
Hydrogen production by water splitting via photocatalysis is cleaner than the traditional methane reforming method. Even though ruthenium oxide is expensive, the small quantities used in this catalyst could make industrial applications cost-effective.
Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOF)
Metal-Organic Frameworks, or MOFs, are crystalline materials composed of metal ions linked by organic ligands to form porous structures. These materials have a very high internal surface area and significant absorption capacity, making them ideal for numerous applications.
MOFs are notable for their ability to be custom-designed by altering the metals and ligands used to achieve specific properties. They are used in various fields, including:
- Gas storage: MOFs can efficiently store gases like hydrogen or carbon dioxide due to their high internal surface area.
- Gas separation: With their varying pore sizes, they can separate different types of gases.
- Catalysis: MOFs can serve as catalysts or catalyst supports to accelerate chemical reactions, such as producing hydrogen from water.
- Pollution control: They can adsorb pollutants, making water and air cleaner.
Thus, MOFs are very promising materials for applications in clean energy and environmental sectors, particularly for hydrogen storage and production, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.