Rocket Lab unveils its plan for reusable rocket and stackable satellites 🚀
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
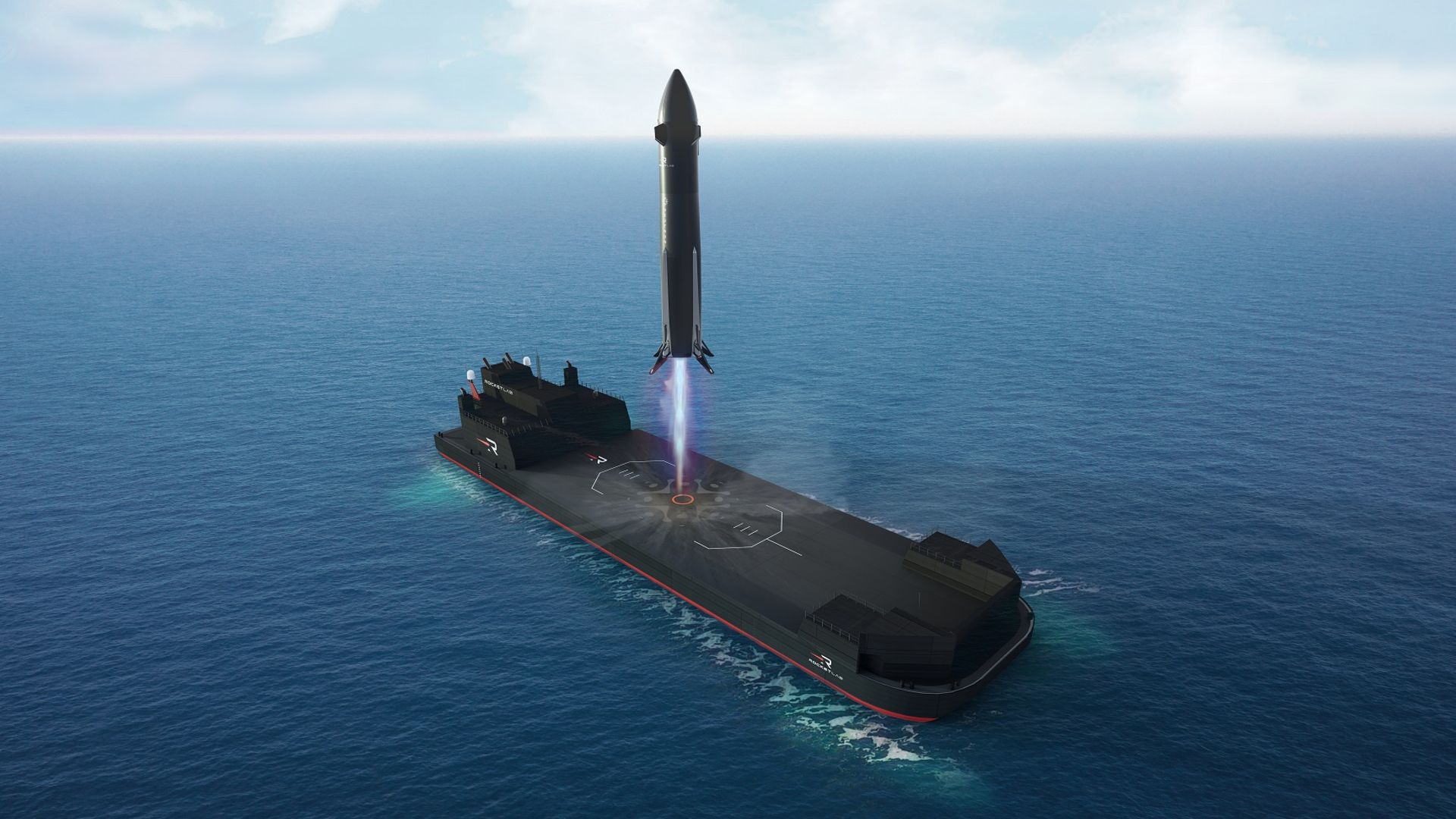

Rocket Lab's new Neutron launcher is designed to be reusable and land on a sea barge for recovery.
Credit: Rocket Lab
Peter Beck, founder and CEO of Rocket Lab, unveiled the progress on Neutron during a recent conference. This launcher aims to meet the growing demand for launch services in the defense, security, and science sectors. The company is working at a sustained pace to adhere to one of the fastest development schedules in history.
Rocket Lab has also introduced a modified offshore barge, named 'Return on Investment', intended to serve as a sea landing platform for Neutron missions. This should increase opportunities for missions requiring maximum performance from the launcher.
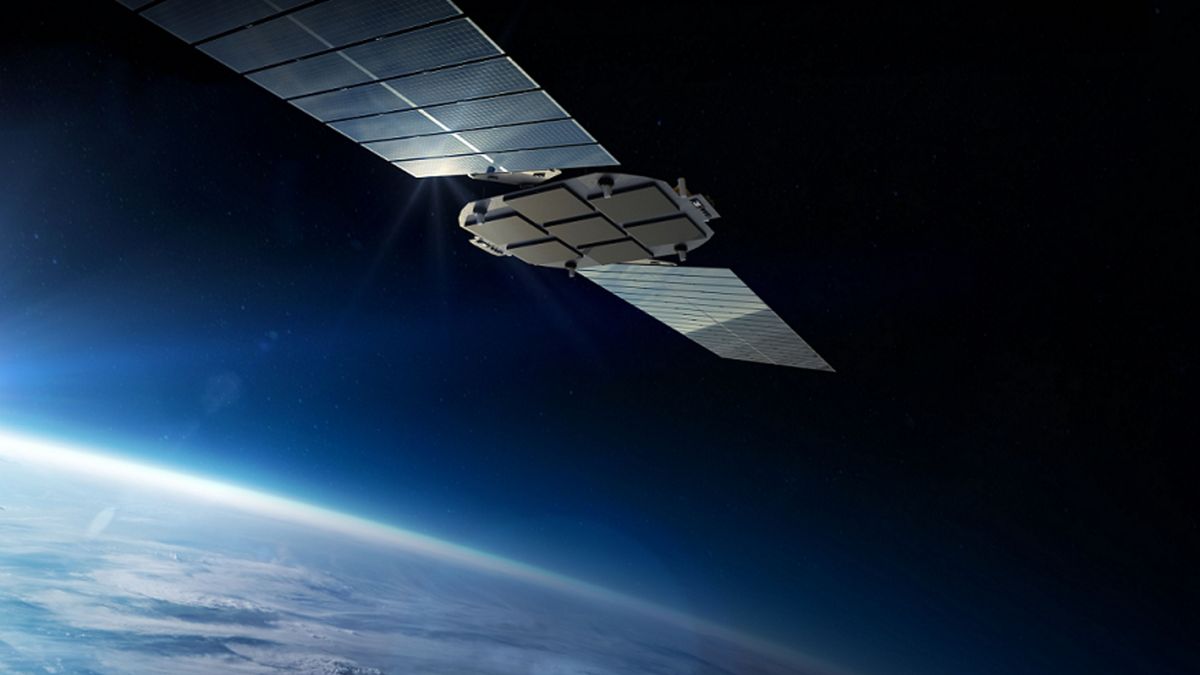

Rocket Lab's design for its new 'Flatellite' satellite in Earth orbit.
Credit: Rocket Lab
In parallel, Rocket Lab announced the development of a new satellite product, the 'Flatellite'. This flat satellite is designed for mass production and is suited for large constellations. Its shape allows for stacking, maximizing the number of satellites per launch.
The CEO described this initiative as a 'bold strategic move' towards realizing Rocket Lab's vision: becoming a full-fledged space company, operating its own constellation and offering services from space.
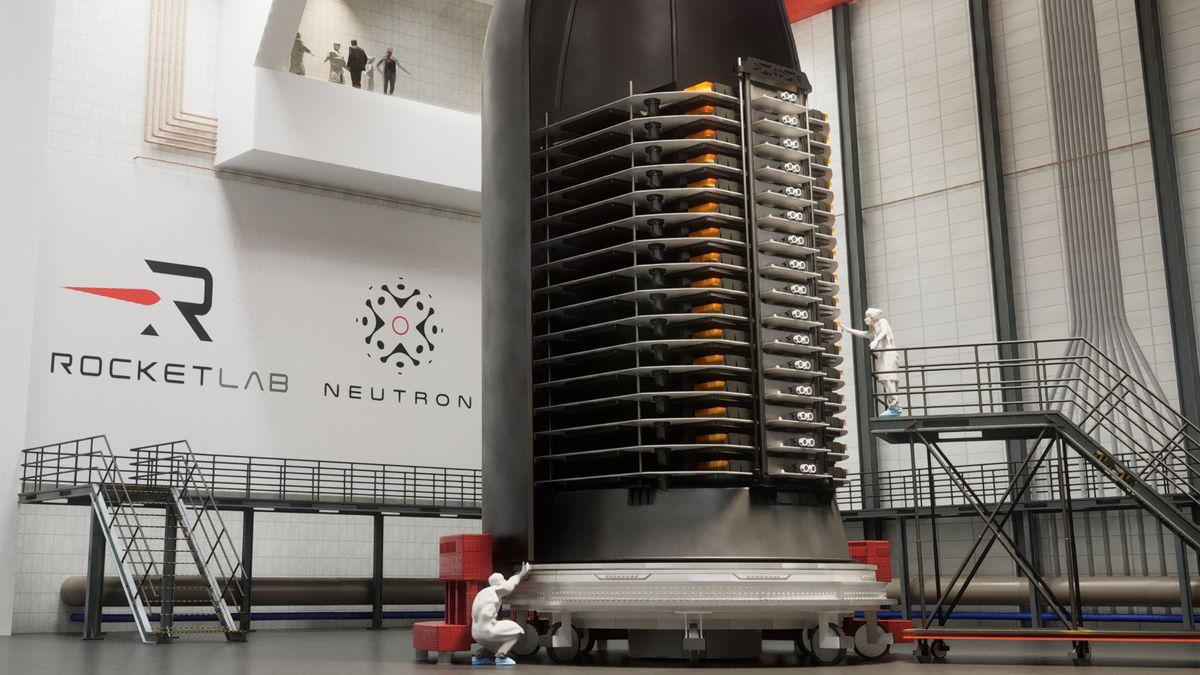
Rocket Lab's plan for its Flatellite satellite product, designed to be launched in stacks for constellation launches.
Credit: Rocket Lab
Currently, Rocket Lab uses its Electron launcher for small satellite missions. The Japanese company iQPS has signed a contract for eight Electron missions planned between 2025 and 2026.
What is a reusable launcher?
A reusable launcher is a type of rocket designed to be used multiple times, unlike traditional launchers which are single-use. This significantly reduces the cost of space missions.
Reusability involves advanced technologies for the safe return and landing of the launcher. Rocket Lab, with its Neutron project, is part of this trend by planning sea landings on a specially modified barge.
This approach requires high-level engineering to ensure the reliability and safety of the launcher after each mission. The economic and environmental benefits of this technology are significant, paving the way for increased accessibility to space.
How do satellite constellations work?
Satellite constellations consist of a group of satellites working together to provide global or regional coverage. They are essential for communications, Earth observation, and navigation.
Rocket Lab, with its new 'Flatellite' product, aims to facilitate the creation of these constellations. Flat satellites can be stacked, allowing multiple units to be launched in a single mission, optimizing costs and efficiency.
This approach is necessary to meet the growing demand for space services, particularly in the fields of defense, security, and scientific research. The ability to produce and launch satellites quickly is a major asset for space companies.