The energy of life: what was thought to be chemical is actually quantum 🌱
Published by Adrien,
Source: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Source: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)

The study, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows that proton transfer is not solely a chemical process. It also involves quantum phenomena, such as electron spin and molecular chirality. This discovery could change our understanding of biological processes.
The researchers used lysozyme crystals for their experiments. They observed that injecting electrons with a specific spin altered proton mobility. This phenomenon is linked to the excitation of chiral phonons, vibrations in the crystal lattice.
The phenomenon, known as the CISS effect (Chiral Induced Spin Selectivity), explains how chiral molecules interact differently with electron spins. This interaction directly influences proton transfer, a process essential to life.
The implications of this discovery are vast. It could lead to the development of new technologies inspired by biological processes. Researchers envision applications in medicine, energy, and nanotechnology.
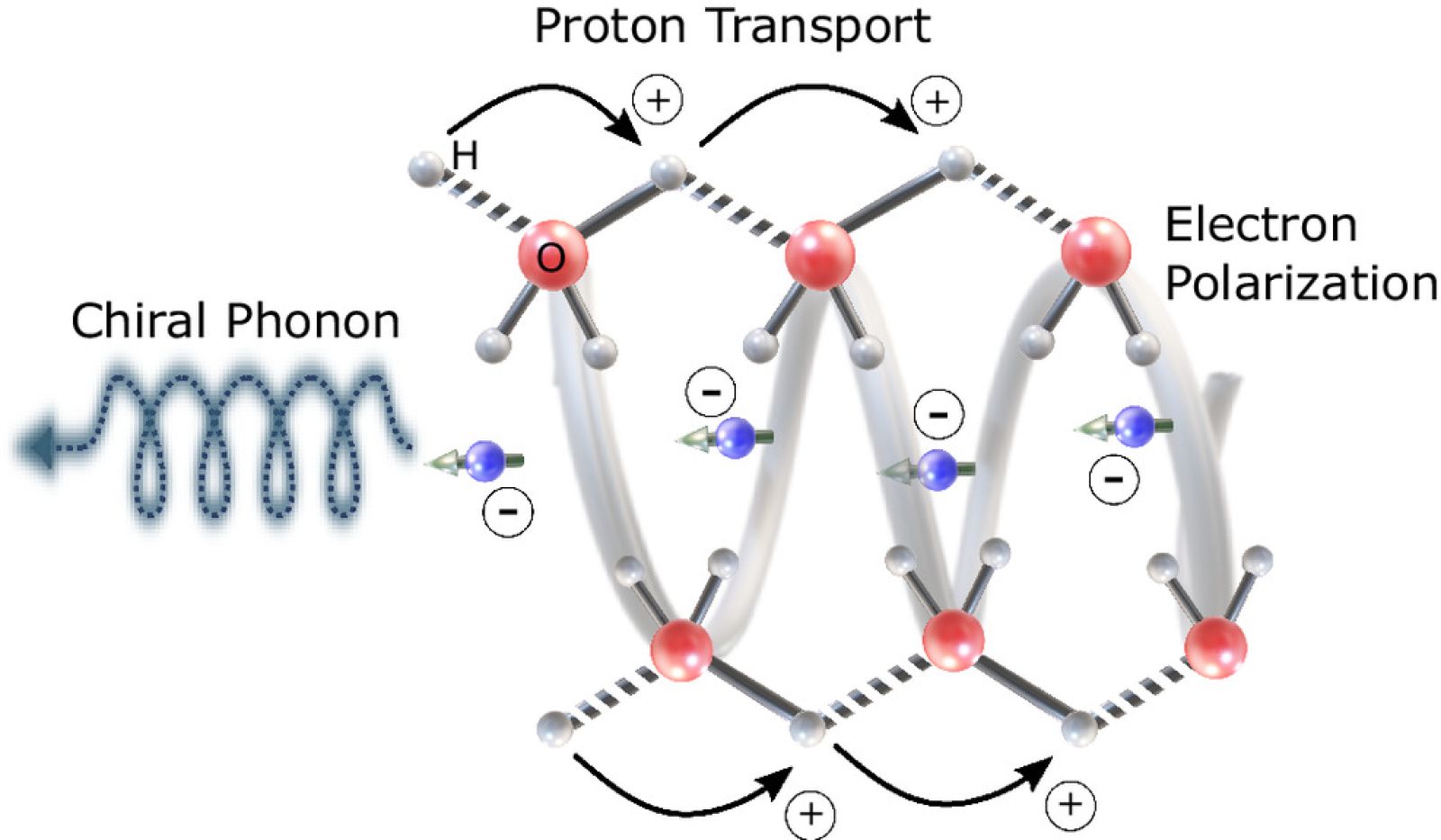
Simplified diagram of a proton transport model. Proton movement is accompanied by electron polarization. In a chiral medium, the CISS effect transforms this electrical polarization into spin polarization. The conservation of angular momentum then generates chiral phonons, which induce spin-selective proton transfer.
The team, led by scientists from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, collaborated with experts from the Weizmann Institute and Ben Gurion University. Their work bridges quantum physics and biochemistry, offering a more complete vision of life's mechanisms.
What is the CISS effect?
The CISS effect, or Chiral Induced Spin Selectivity, is a quantum phenomenon where chiral molecules filter electrons based on their spin. This means these molecules can prefer one electron spin over another, thereby influencing chemical reactions.
This effect is particularly important in biological systems, where molecular chirality is omnipresent. It explains how certain reactions can be more efficient or selective depending on the spin of the involved electrons.
Potential applications of the CISS effect are numerous, ranging from the design of new materials to a deeper understanding of biological mechanisms. It's a rapidly expanding research field at the frontier between physics and biology.