Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
This study, co-directed by Corinne Cayrol and Jean-Philippe Girard, was published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine on April 10th.
Image Wikimedia
The inflammation process plays a crucial role in respiratory allergic diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis. While the pulmonary epithelium, this layer of cells forming the inner surface of the lungs, is acknowledged as a key player in respiratory inflammation underlying these diseases, the underlying mechanisms are still poorly understood.
A research team has identified one of the molecules responsible for triggering the allergic reaction, in a study co-led by two CNRS and Inserm scientists working at the Institute of Pharmacology and Structural Biology (CNRS/University of Toulouse III - Paul Sabatier).
This molecule, belonging to the alarmin family and named TL1A, is released by pulmonary epithelium cells minutes after exposure to a mold-type allergen. It cooperates with another alarmin, interleukin-33, to alert the immune system of the presence of an allergen. This double alarm signal will stimulate the activity of immune cells, which will then trigger a cascade of chain reactions responsible for allergic inflammation.
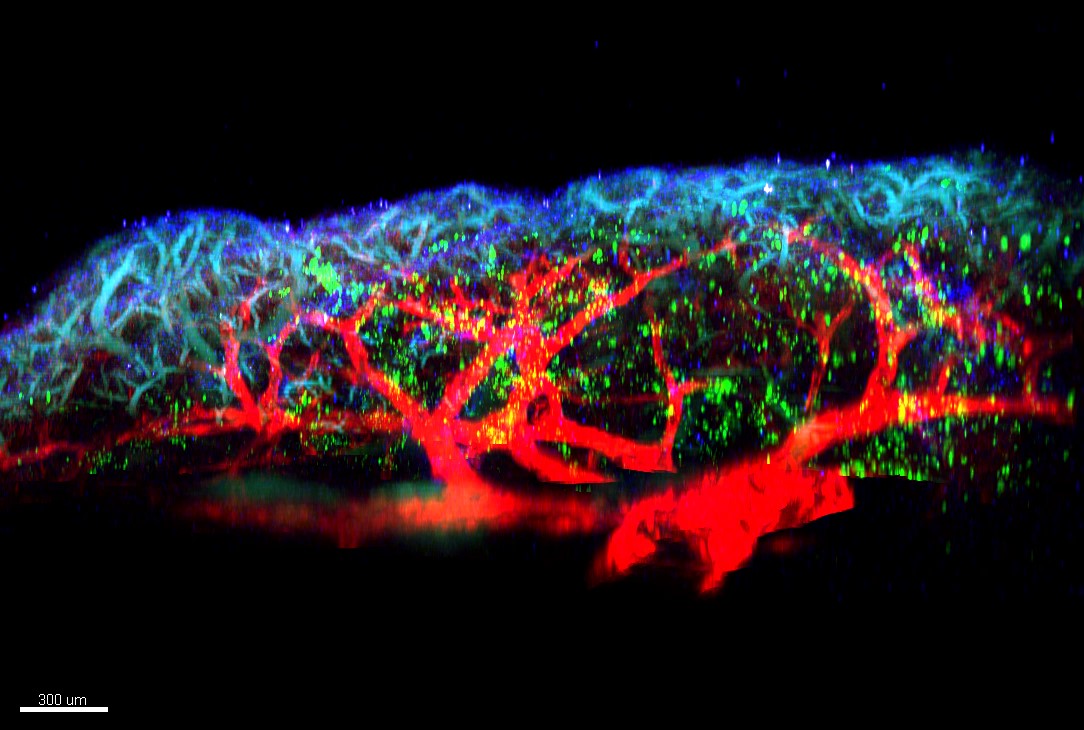
Microscopy visualization of immune cells (in green) activated by the alarmins TL1A and interleukin-33 during the onset of allergic inflammation in the lungs. The "ILC2s" immune cells produce large amounts of interleukin-9, a key mediator of allergic inflammation. They are located near the collagen fibers (in blue) and blood vessels of the lung (in red).
© Jean-Philippe GIRARD - IPBS (CNRS/UT3 Paul Sabatier).
Therefore, alarmins represent major therapeutic targets for the treatment of respiratory allergic diseases. In a few years, treatments based on antibodies blocking the alarmin TL1A could benefit patients suffering from severe asthma or other allergic diseases. In France, at least 17 million people are affected by allergic diseases. The most serious forms of asthma are responsible for several hundred deaths every year.