Mars and Regulus: a duo currently visible to the naked eye in the sky
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
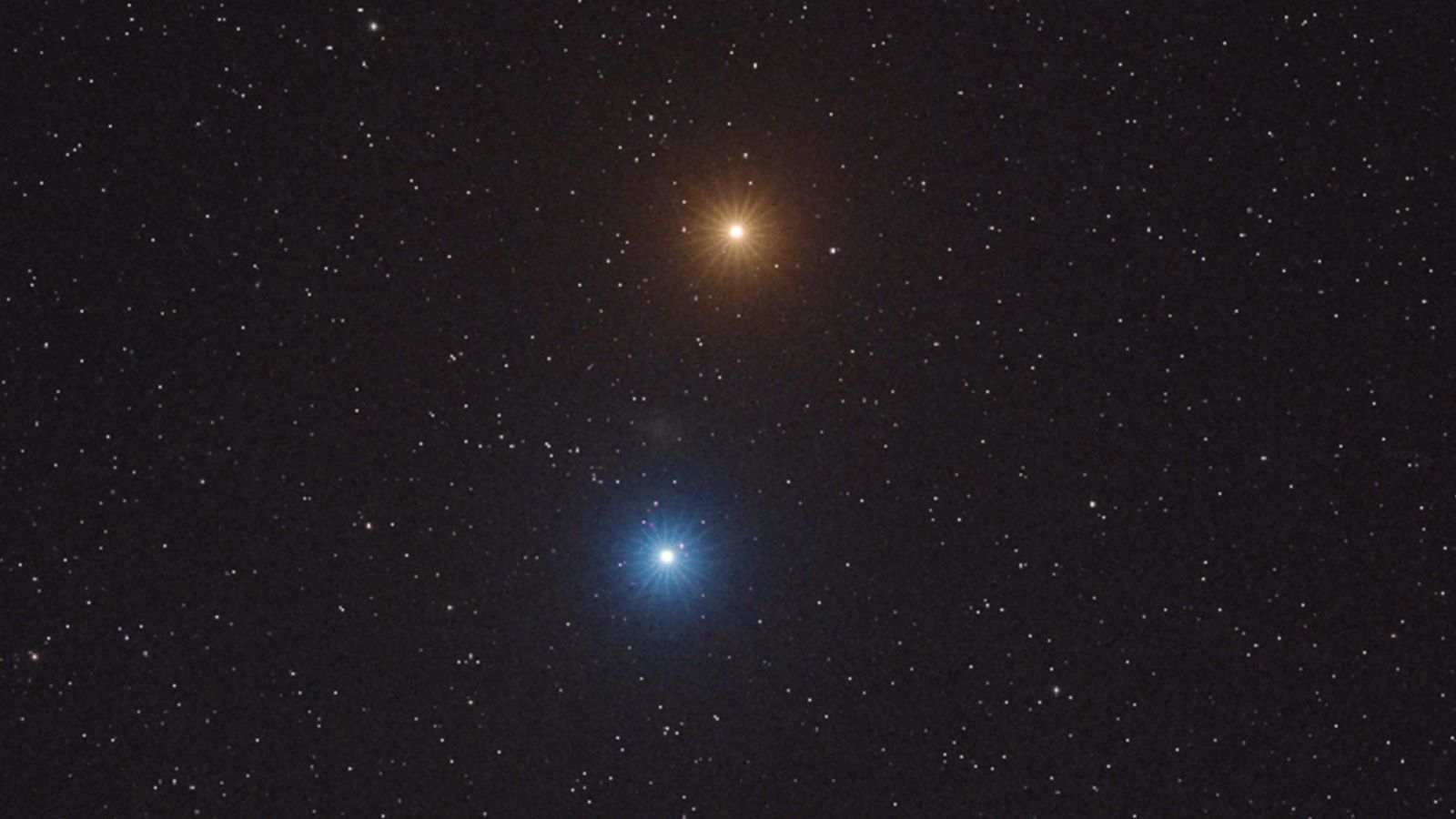

On June 16, the Virtual Telescope Project captured a stunning photo of Mars (top) and Regulus (bottom) shining side by side in the night sky.
Credit: Virtual Telescope Project
Regulus, the brightest star in the constellation Leo, emits light from a system containing four stars. Located approximately 79 light-years from Earth, this system is marked by a blue hue due to its largest star, a blue subgiant. Mars, on the other hand, shines intensely because of its favorable position relative to Earth and the Sun.
The conjunction between Mars and Regulus peaked on June 17, when the two celestial bodies were less than one degree apart. This apparent proximity results from their respective positions in the sky, offering a striking color contrast between Mars' red and Regulus' blue.
Between Mars and Regulus, an attentive observer can spot a faint, fuzzy patch of light corresponding to the dwarf galaxy Leo I. This rare sight adds another dimension to the spectacle.
The year 2025 is marked by several notable astronomical events, including this conjunction between Mars and Regulus. These moments offer everyone the opportunity to admire the beauty of the sky with just the naked eye.
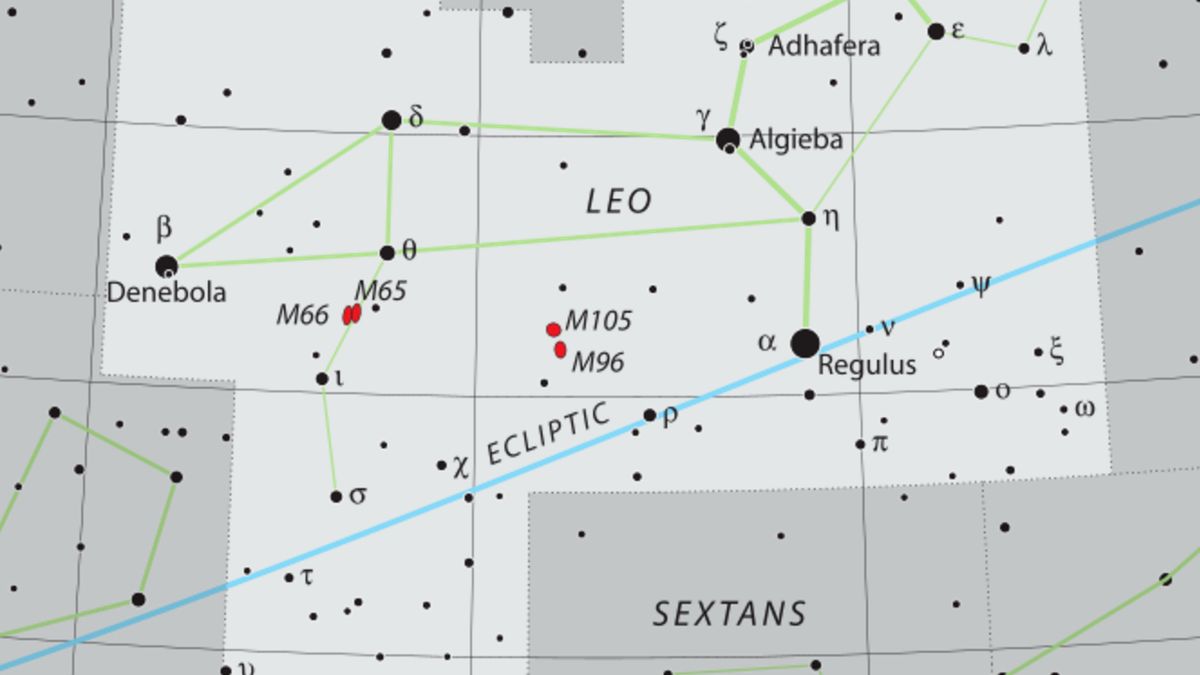
Regulus is located very close to the ecliptic, which explains its frequent appearance near planets and the Moon.
Credit: IAU/Wikimedia
What is a conjunction in astronomy?
A conjunction occurs when two celestial bodies appear close to each other in the night sky as seen from Earth. This phenomenon is due to their relative alignment from our perspective, even though they may be separated by vast distances in space.
Conjunctions can involve planets, stars, the Moon, or even asteroids. They provide opportunities for astronomical observations and photography, highlighting the dynamics of our Solar System.
Though conjunctions are frequent, some are more spectacular than others, especially when the objects involved are bright or exhibit marked color contrasts.
Why does Mars appear red in the night sky?
Mars owes its characteristic red color to the presence of iron oxide, commonly known as rust, on its surface. This distinctive hue is visible from Earth, especially when the planet is close to us and well-lit by the Sun.
Mars' brightness varies significantly depending on its distance from Earth and its position relative to the Sun. When it is in opposition—aligned with Earth and the Sun—Mars appears particularly bright and red.
This reddish coloration has been noted by humans since ancient times, inspiring myths and legends. Today, it also serves as a visual marker for identifying the planet in the night sky.