Over 50,000 mysterious DNA structures discovered in our genome: what are the impacts?
Published by Cédric,
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: The EMBO Journal
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: The EMBO Journal
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
A study uncovers the surprising presence of over 50,000 enigmatic structures within our genome. These formations, known as i-motifs, could revolutionize our understanding of genetic regulation mechanisms.
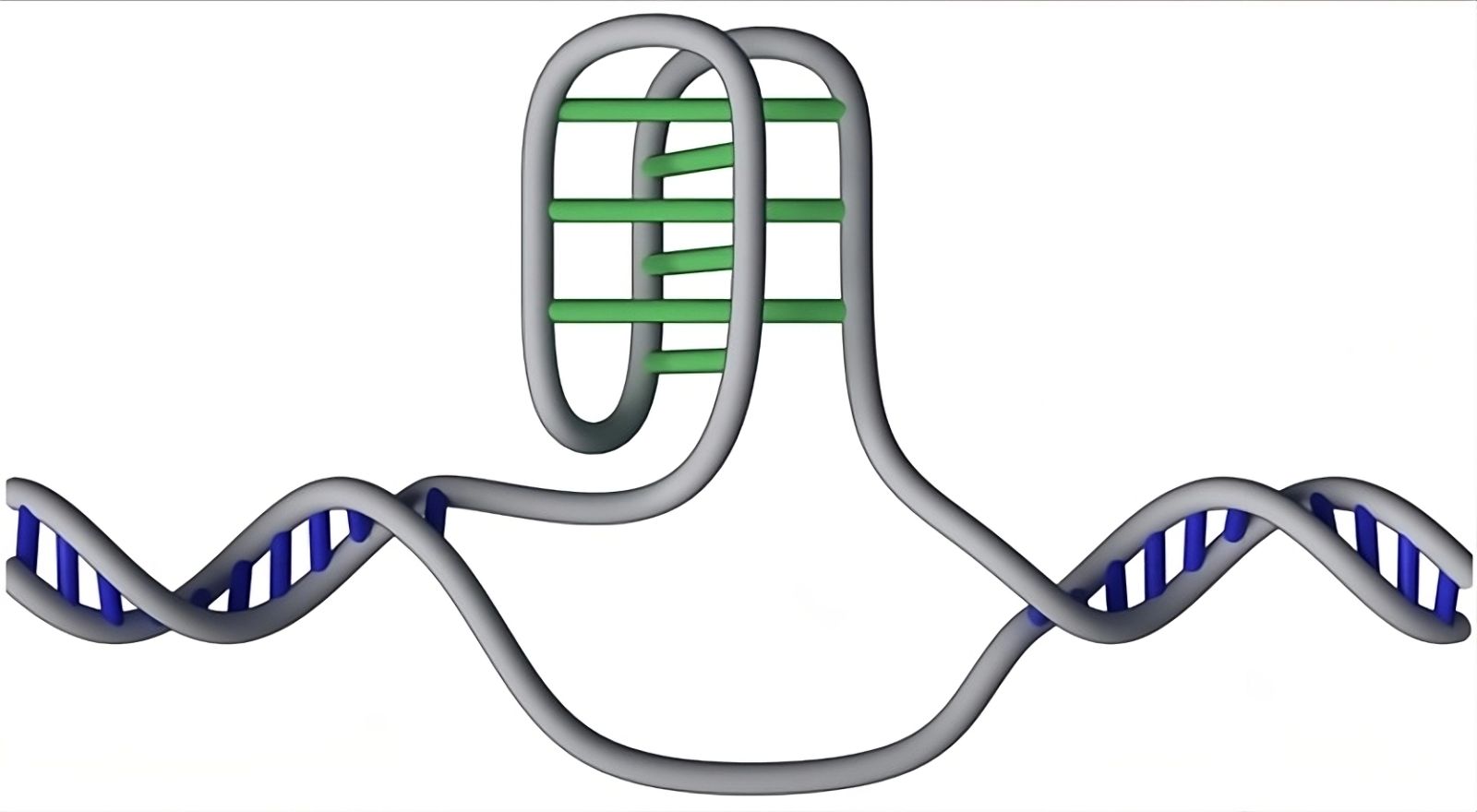
The knot-like "i" structure protruding from the DNA double helix has been mapped at 50,000 locations in the human genome
DNA, often depicted as a double helix, actually conceals more complex structures. A team of researchers from the Garvan Institute of Medical Research has recently mapped these i-motifs, revealing their abundance and potential role in controlling genes and diseases.
I-motifs are four-stranded structures formed when cytosine bases on the same DNA strand bond with each other. These formations are distinct from the famous double helix. Their presence has long been debated, but their identification in living cells in 2018 by the Garvan team marked a significant breakthrough.
The current study, published in The EMBO Journal, identified over 50,000 i-motif sites throughout the human genome. Researchers used an innovative antibody to mark and locate these structures, confirming their role in gene regulation.
These i-motifs are not randomly distributed. They concentrate in crucial genomic regions, such as promoters and telomeric regions, which are vital for gene activity. The findings suggest that these structures play a key role in the cell cycle and in the regulation of oncogenes.
The study also highlights the relationship between i-motifs and certain genes involved in hard-to-treat cancers. I-motifs often appear near oncogene regions, such as the MYC gene, which opens new avenues for targeted therapeutic approaches.
The widespread presence of these structures in significant genomic areas could offer new opportunities for the development of diagnostics and treatments. By specifically targeting i-motifs, it could become possible to modulate gene expression and thus expand the available therapeutic options.