Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
The study published in Radiology explores how fans' brains activate differently depending on their favorite team's results. By observing sixty male fans using functional magnetic resonance imaging, researchers were able to map the brain areas involved in these emotional reactions. The participants, selected for their attachment to rival clubs, watched footage of goals scored by different teams while scientists measured their neural activity. This innovative approach captures the brain snapshots that occur during key moments of a match.
The passion of soccer fans reveals the hidden brain patterns of fandom and how early experiences can encourage or prevent it.
Credit: Shutterstock
When the favorite team scores against its historic rival, the brain circuits related to reward light up in a particularly intense way. This enhanced activation of the natural gratification system explains why fans feel such deep joy during important victories. Conversely, when the opponent scores, the brain regions responsible for cognitive control show a surprising decrease in activity. This neurobiological phenomenon could explain why even usually rational people can lose their temper during matches.
Researchers found that these brain reactions were more pronounced in the most passionate fans, those who show a strong sense of belonging to their group. This neural connection between social identity and emotional reactions suggests that our brain processes collective successes as personal rewards. The sense of belonging to a fan community activates brain mechanisms similar to those observed in other forms of group engagement, whether political or religious affiliations.
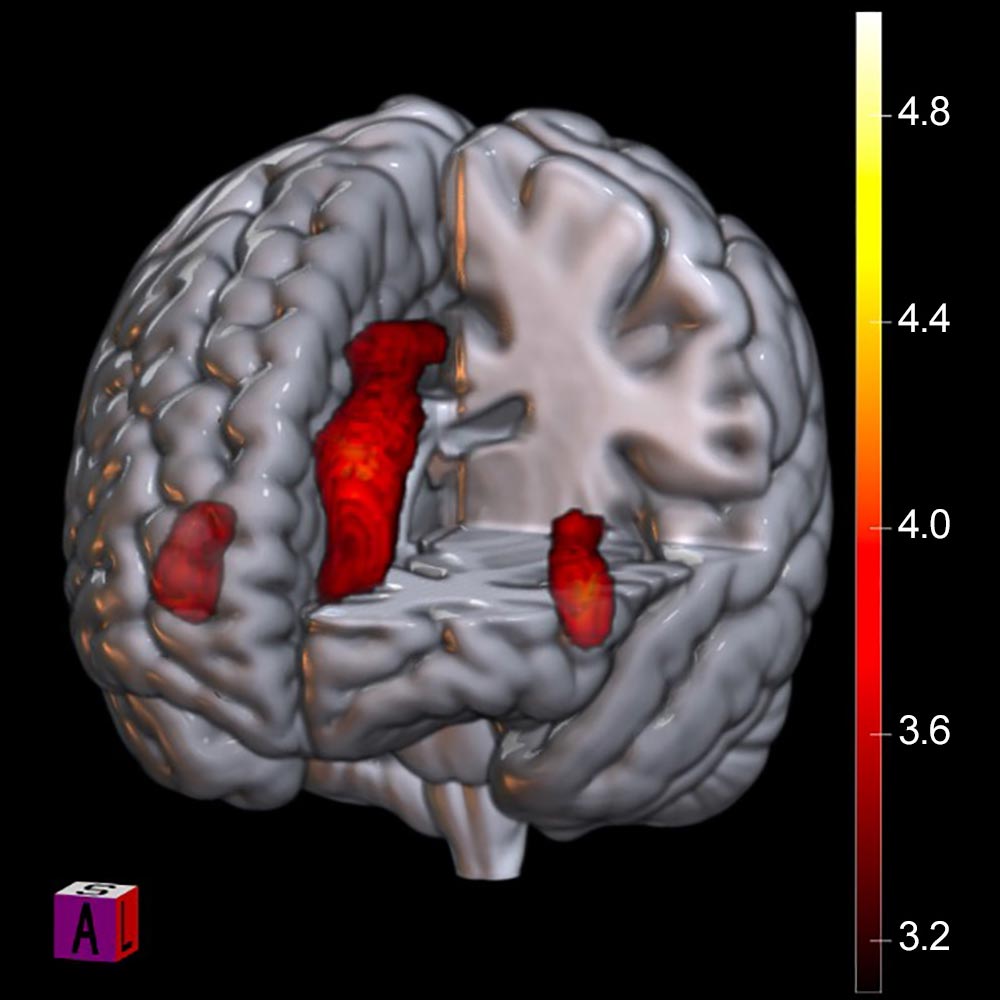
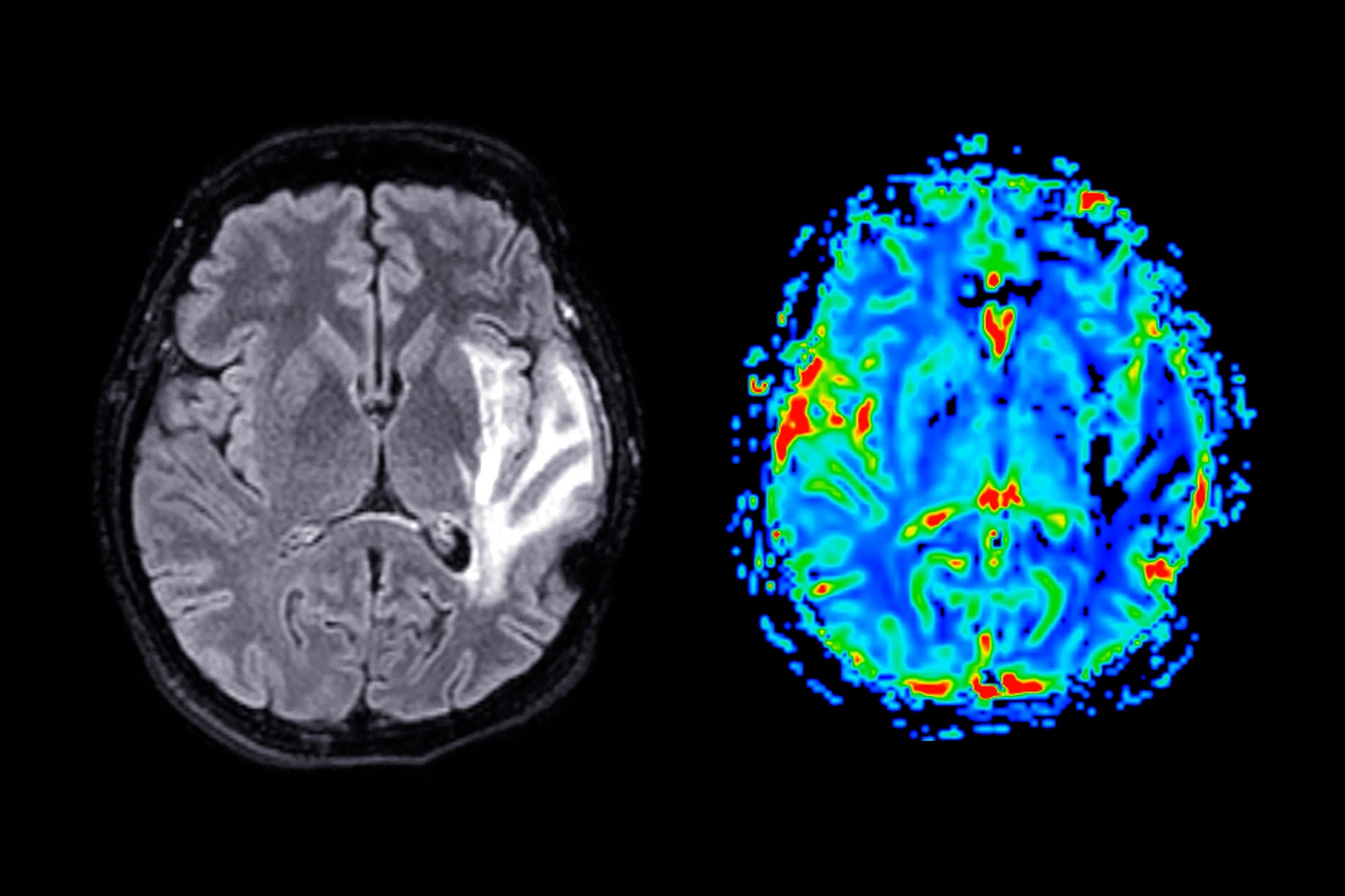
Representation of the brain effects of a significant defeat. The salience network deactivates during an important defeat. The colored bar represents Z values.
Credit: Radiological Society of North America (RSNA)
The implications of these discoveries extend far beyond the sports context. The same brain patterns observed in soccer fans could explain certain behaviors in political conflicts or social tensions. When our collective identity is threatened, our brain seems to switch to a mode where the search for reward overrides our control capacity. This understanding opens perspectives for better managing crowds during events with high emotional tension.
The most significant aspect of this research concerns the origin of these brain circuits. Scientists emphasize that these mechanisms are forged from childhood, influenced by the quality of parental care, exposure to stress, and social learning. Our ability to manage emotions related to group belonging would therefore be largely determined by our early experiences. This developmental perspective suggests that societies that invest in children's well-being could prevent certain forms of excessive fanaticism.
Research on fans' brains thus offers us a unique window into the universal mechanisms that govern our social affiliations. By understanding how our brain reacts to collective victories and defeats, we can better grasp the dynamics that animate human groups in various contexts, from stadiums to political arenas.
The brain's reward system
Our brain has a specialized network that makes us feel pleasure during positive experiences. This reward system naturally activates when we eat delicious food, receive a compliment, or experience a pleasant moment. In soccer fans, this brain area lights up particularly when their team scores a goal, creating an intense feeling of happiness that strengthens their attachment to the group.
Researchers observed that this activation is even stronger when the goal is scored against a historic rival. This amplification suggests that the brain processes collective successes as personal victories, blending individual identity and group belonging. This mechanism explains why fans feel such deep pride during their team's triumphs, as if they had personally contributed to the performance.
This reward system is not limited to the sports domain. It comes into play in all situations where we identify with a group, whether it's an online community, a work team, or a political cause. Understanding its functioning helps explain why collective successes can provoke such powerful emotions, sometimes disproportionate to our actual involvement.
The most surprising discovery concerns the interaction between this reward system and our control capacity. When the reward is too intense, it can temporarily decrease our critical judgment, explaining certain impulsive behaviors observed in the most passionate fans. This brain dynamic illuminates the mechanisms underlying collective enthusiasm in various social contexts.
Cognitive control and its limits
Our brain has sophisticated mechanisms to regulate our emotions and behaviors, grouped under the term cognitive control. These functions help us stay calm under pressure, make thoughtful decisions, and adapt our reactions to situations. In the sports context, this system normally allows fans to manage their disappointment during a defeat or their excitement during a victory.
However, the study reveals that during important defeats against a rival, this control capacity shows a surprising decrease in activity. The brain region responsible for moderating emotional reactions seems temporarily less effective, which could explain why even usually measured people can have excessive reactions during matches. This phenomenon appears particularly marked in the most committed fans.
This temporary decline in cognitive control does not mean that fans completely lose their judgment capacity. It's rather a temporary imbalance between different brain areas, where emotions temporarily override reason. This dynamic illuminates why sporting events can sometimes generate unpredictable collective reactions, even among normally rational individuals.
Understanding these mechanisms opens interesting perspectives for crowd management and prevention of excessive behaviors. By identifying the moments when cognitive control is most vulnerable, it becomes possible to develop strategies to help individuals maintain their self-control, whether in stadiums or in other social contexts where collective emotions can take over.