This innovative window transforms rain into electricity, and much more...
Published by Cédric,
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: Nano Energy
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: Nano Energy
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)

Developed to address various environmental challenges, this smart window integrates advanced technologies to optimize thermal and energy management. The innovation is based on a complex material combining the properties of silver and ITO (indium tin oxide). These layers maintain transparency while reflecting infrared heat.
One of the most fascinating aspects is the window's ability to generate electricity via raindrops. Using a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), each water droplet impacting the surface generates energy, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional photovoltaic systems.
The prototype also ensures radiative cooling without consuming electricity, a remarkable advancement compared to conventional windows that lose transparency to enhance energy efficiency. This cooling is achieved without refrigerants, making it more eco-friendly and economical.
Additionally, the window features an automatic defrosting function via the Joule effect. The window's transparent electrodes heat up quickly to remove ice or frost, ensuring clear visibility even in winter. This mechanism is integrated without requiring an additional external energy source.
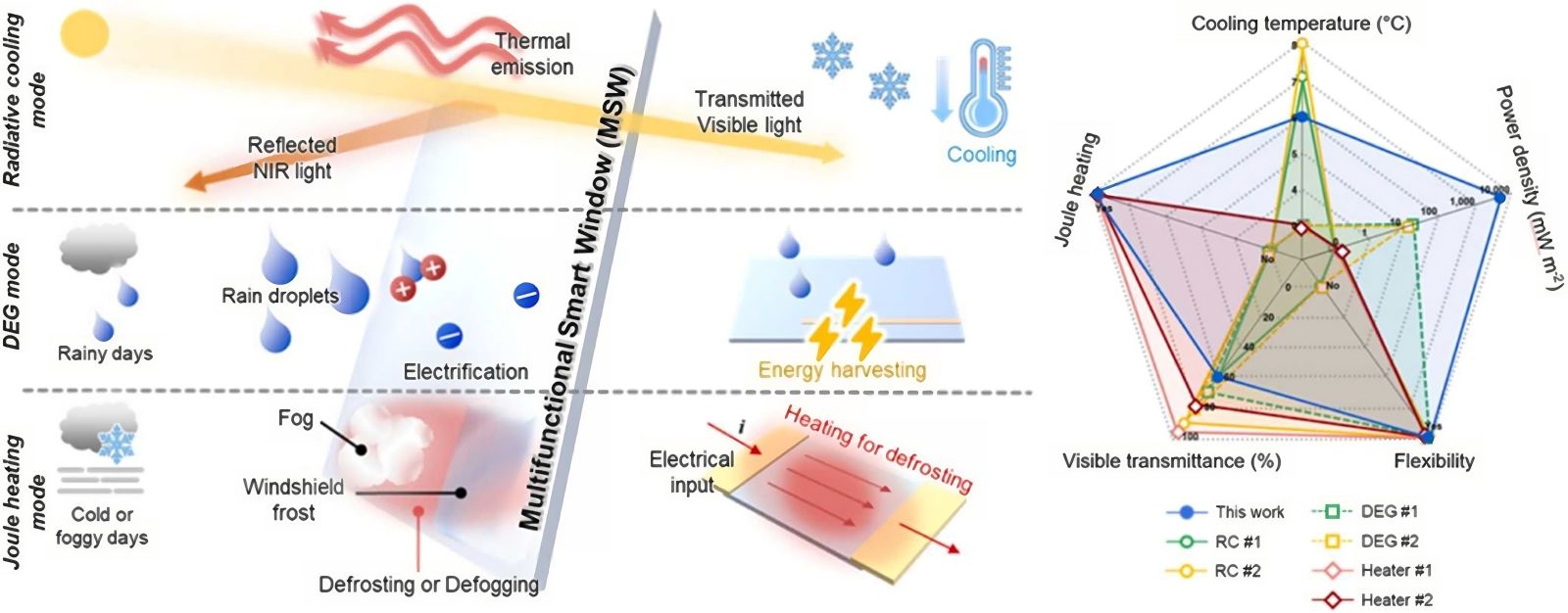
Tests have revealed impressive performance: under simulated rainy conditions, each raindrop generated 8.3 watts per square meter. The internal temperature of buildings equipped with this technology can be reduced by about 13°F (7°C) compared to ordinary windows, even in direct sunlight.
The project, led by Professor Seung Hwan Ko, aims to go beyond zero-energy buildings to achieve positive-energy building goals. This technological advancement could not only enhance the energy efficiency of buildings but also play a crucial role in the transition to more sustainable energy sources.
Although this prototype is not yet available on the market, it represents a significant advance in the search for innovative and environmentally friendly energy solutions. The smart window could well become a key element of sustainable architecture tomorrow.