Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
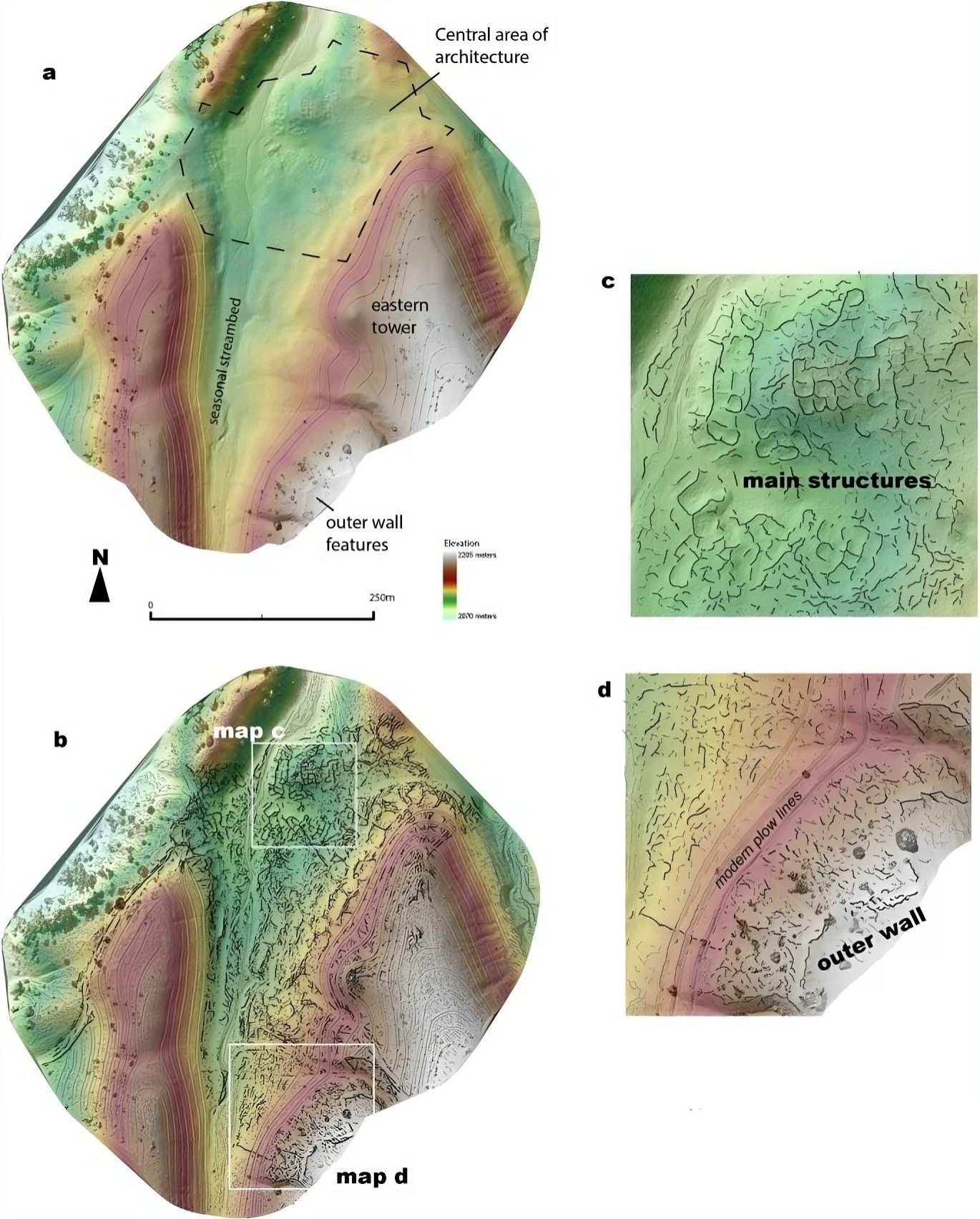
Detailed Lidar and ridgeline mapping, Tashbulak.
A team of researchers led by Michael Frachetti and Farhod Maksudov began their investigation over a decade ago. By using drones and LiDAR technology, they revealed structures buried beneath mountainous landscapes. The images obtained provide us with insights into the history of commercial exchanges.
The LiDAR technique has allowed for the mapping of these hard-to-reach sites. Thanks to this technology, researchers were able to identify complex structures, including fortifications and public spaces, revealing advanced urban planning.
The two cities are located at an unusual altitude for urban settlements. At about 7,200 feet (2,200 meters), Tugunbulak is the highest known medieval city in Central Asia. This discovery challenges the norms of urbanization in this region. Contrary to popular belief, trade routes did, in fact, pass through these mountains. The study's results show that these cities were dynamic hubs, driven by trade and craftsmanship, between the 6th and 11th centuries AD.
Tugunbulak, covering 300 acres (120 hectares), was a true economic center. Early excavations indicate that this city was a site for metallurgical production, exploiting surrounding resources. This could have contributed to its development and prosperity.
Tashbulak, though smaller, had a unique cemetery, reflecting the rise of Islam in the region. Its tombs, among the oldest, reveal a strong spiritual connection, attracting individuals from various backgrounds.
The reasons for the abandonment of these cities remain unknown. No signs of destruction have been observed, leaving room for speculation about political or climatic changes that may have influenced their decline.
The rediscovery of Tugunbulak and Tashbulak challenges our understanding of medieval civilizations. These mountain cities, long overlooked, shed light on the diversity of Central Asian societies.
What is LiDAR technology?
LiDAR technology, short for "Light Detection and Ranging", is a remote sensing method that uses lasers to measure distances. By sending out light pulses and analyzing the time it takes for these pulses to return, LiDAR can create detailed 3D maps of landscapes.
This technology is particularly useful in hard-to-reach environments, such as mountainous areas. In archaeology, it helps to reveal hidden structures, providing valuable information on historical sites that were previously inaccessible. Thanks to LiDAR, major discoveries, like those of the medieval cities of Tugunbulak and Tashbulak, are now possible, changing our understanding of past civilizations.