Pithecia pithecia - Définition
Source: Wikipédia sous licence CC-BY-SA 3.0.
La liste des auteurs de cet article est disponible ici.
La liste des auteurs de cet article est disponible ici.
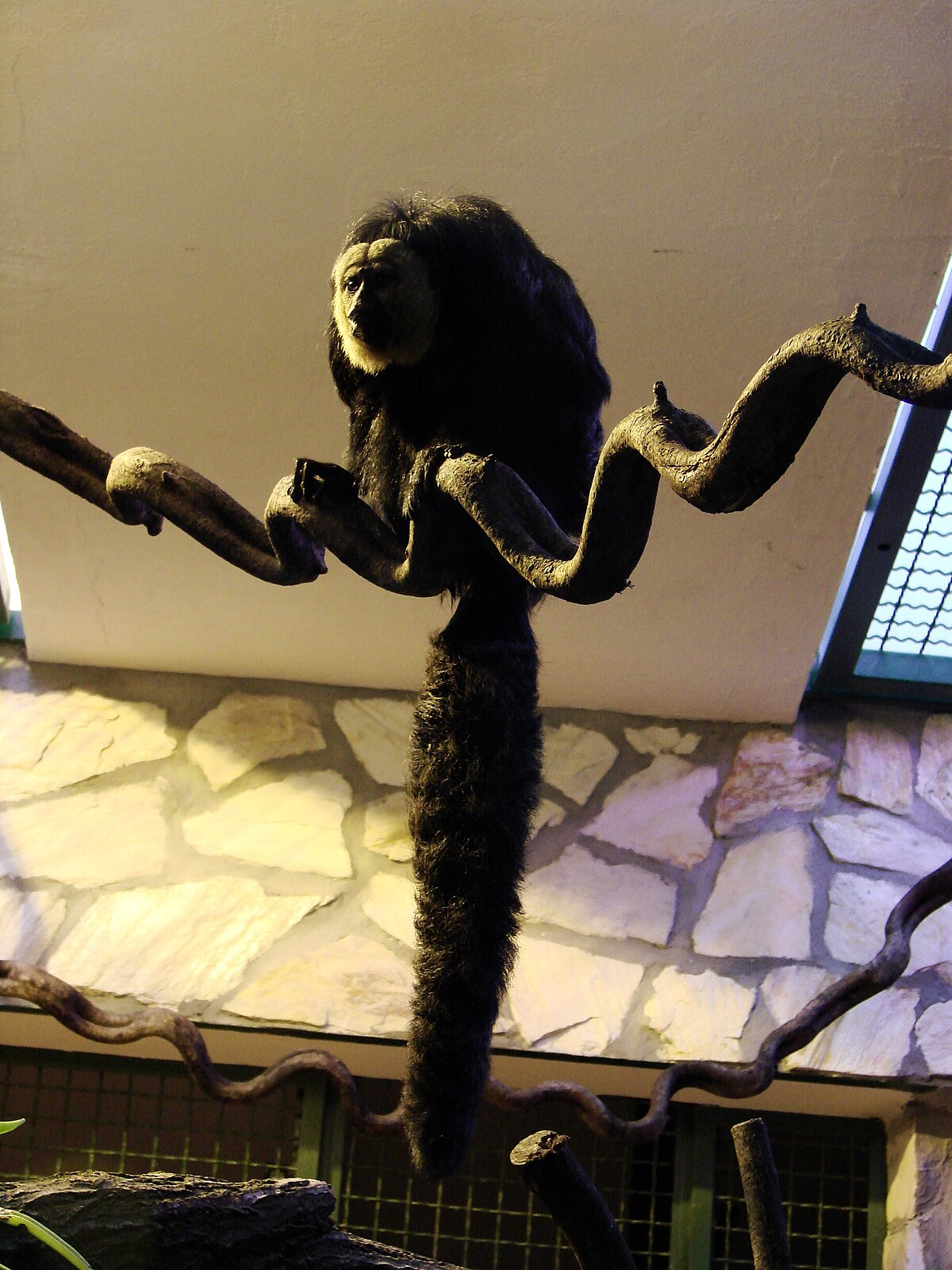
| Saki à face blanche | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

| |||||||||
| Classification | |||||||||
| Règne | Animalia | ||||||||
| Embranchement | Chordata | ||||||||
| Sous-embr. | Vertebrata | ||||||||
| Classe | Mammalia | ||||||||
| Sous-classe | Theria | ||||||||
| Infra-classe | Eutheria | ||||||||
| Ordre | Primates | ||||||||
| Famille | Pitheciidae | ||||||||
| Sous-famille | Pitheciinae | ||||||||
| Genre | Pithecia | ||||||||
| Nom binominal | |||||||||
| Pithecia pithecia (Linnaeus, 1766) | |||||||||
| Statut de conservation IUCN : | |||||||||
| | |||||||||
| | |||||||||
Le Saki à face blanche (Pithecia pithecia) est un primate du nord de l'amérique du sud (Guyane française, Guyana, Surinam, est du Vénézuela, nord du Brésil).