Cephalophinae - Définition
Source: Wikipédia sous licence CC-BY-SA 3.0.
La liste des auteurs de cet article est disponible ici.
La liste des auteurs de cet article est disponible ici.
| Cephalophinae | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| Classification | |||||||||
| Règne | Animalia | ||||||||
| Embranchement | Chordata | ||||||||
| Classe | Mammalia | ||||||||
| Infra-classe | Eutheria | ||||||||
| Cohorte | Laurasiatheria | ||||||||
| Ordre | Cetartiodactyla | ||||||||
| Sous-ordre | Ruminantia | ||||||||
| Famille | Bovidae | ||||||||
| Clade | Aegodontia | ||||||||
| Sous-famille | |||||||||
| Cephalophinae Blyth, 1863 | |||||||||
| Tribus de rang inférieur | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| | |||||||||
| | |||||||||
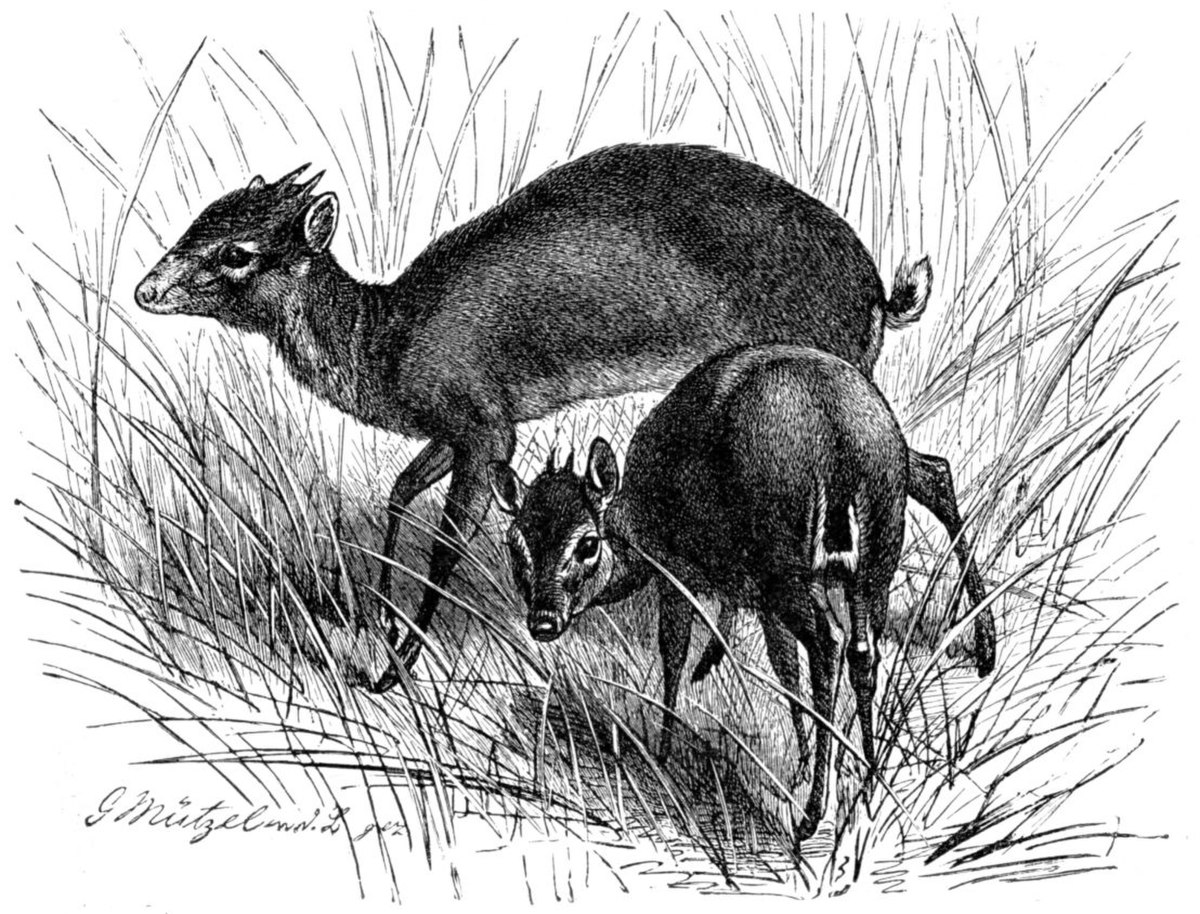
Les Cephalophinae forment une sous-famille de bovidés.
Dans son acceptation classique, elle correspond aux céphalophes ou duikers, répartis sur trois genres :
- Philantomba ((C. H. Smith, 1827), Grubb et al., 1998)
- Sylvicapra (Ogilby, 1837)
- Cephalophus (Hamilton Smith, 1827)
D'un point de vue phylogénétique, on connecte les Cephalophini aux Reduncini.
| Bovidae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||