Flavone (groupe) - Définition
Source: Wikipédia sous licence CC-BY-SA 3.0.
La liste des auteurs de cet article est disponible ici.
La liste des auteurs de cet article est disponible ici.
Introduction
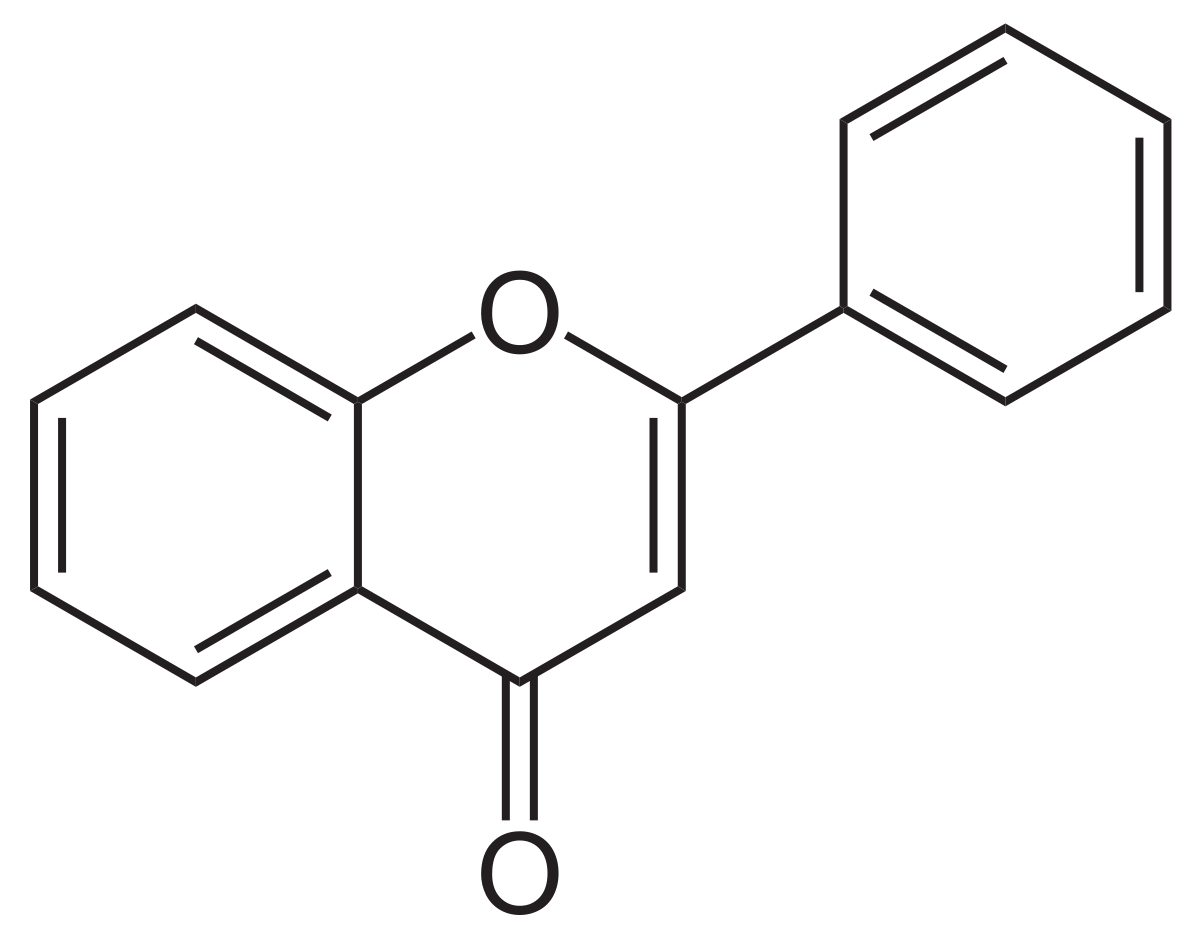
Les flavones sont une sous-famille des flavonoïdes dont la structure est basée sur la flavone (2-phényl-1-benzopyran-4-one ou 2-phénylchromèn-4-one). Ce sont des colorant végétaux jaunes dont environ 300 composés naturels sont connus. Comme d'autres flavonoïdes (hyperoside, quercitrine), ils sont parfois présents sous forme d'hétérosides solubles dans l'eau. On les trouve parfois comme co-pigment avec les anthocyanes.
Les flavones 3-hydroxylées (portant un groupe alcool sur le carbone 3) sont appelées flavonols et forment une autre sous-famille des flavonoïdes.
Principales flavones
Flavones naturelles
| Nom | Structure | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R3' | R4' | R5' | CAS | Nom IUPAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavone |
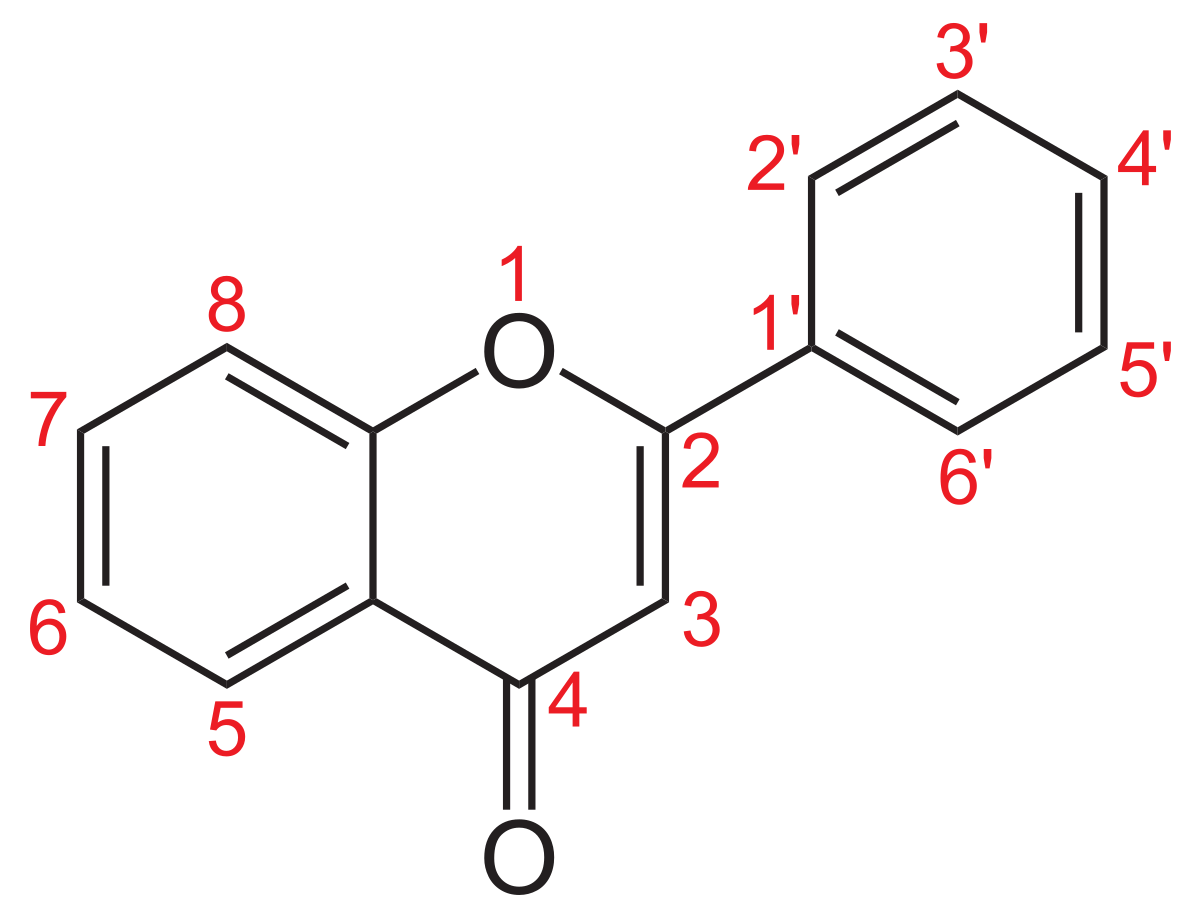
| H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 2-phénylchromèn-4-one | |
| Apigénine | OH | H | OH | H | H | OH | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Acacétine | OH | H | OH | H | H | OCH3 | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-méthoxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Baicaléine | OH | OH | OH | H | H | H | H | 5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-phénylchromèn-4-one | ||
| Chrysine | OH | H | OH | H | H | H | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phénylchromèn-4-one | ||
| Chrysoériol | OH | H | OH | H | OCH3 | OH | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-méthoxy-phényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Diosmétine | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OCH3 | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Eupatiline | OH | OCH3 | OH | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4-diméthoxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Eupatorine | OH | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | OH | OCH3 | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-6-méthoxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Genkwanine | OH | H | OCH3 | H | H | OH | H | 5-hydroxy-7-méthoxy-2-(4-hydroxy-phényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| 6-hydroxyflavone | H | OH | OH | H | H | H | H | 6-hydroxy-2-phénylchromèn-4-one | ||
| Lutéoline | OH | H | OH | H | OH | OH | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Nobilétine | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | 5,6,7,8-téraméthoxy-2-(3,4-méthoxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Oroxyline A | OH | OCH3 | OH | H | H | H | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-6-méhtoxy-2-phénylchromèn-4-one | ||
| Scutellaréine | OH | OH | OH | H | H | OH | H | 5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Sinensétine | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | 5,6,7-triméthoxy-2-(3,4-diméthoxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Tangeritine | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | H | 5,6,7,8-tétraméthoxy-2-(4-méthoxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Techtochrysine | OH | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | 5-hydroxy-7-méthoxy-2-phénylchromèn-4-one | ||
| Tricine | OH | H | OH | H | OCH3 | OH | OCH3 | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diméthoxyphényl)chromèn-4-one | ||
| Wogonine | OH | H | OH | OCH3 | H | H | H | 5,7-dihydroxy-8-méhtoxy-2-phénylchromèn-4-one |
Flavones synthétiques
De nombreuses flavones ont été synthétisées et servent par exemple de médicament. On peut notamment citer le flavoxate la diosmine (hétéroside) ou encore l'hidrosmine.
Hétérosides de flavones
| Hétéroside | Aglycone | R6 | R7 | R8 | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apiine | Apigénine | apioglucose | |||
| Apigétrine | Apigénine | glucose | |||
| Baicaline | Baicaléine | acide glucuronique | |||
| Cynaroside | Lutéoline | glucose | |||
| Diosmine | Diosmétine | rutinose | |||
| Orientine | Lutéoline | glucose | |||
| Isoorientine | Lutéoline | glucose | |||
| Oroxindine | Wogonine | acide glucuronique | |||
| Rhoifoline | Apigénine | néohespéridose | |||
| Scutellarine | Scutellaréine | acide glucuronique | |||
| Tetuine | Baicaléine | glucose | |||
| Véronicastroside | Lutéoline | rutinose | |||
| Vitexine | Apigénine | glucose | |||
| Isovitexin | Apigénine | glucose |